What are the Different Types of Diabetes mellitus – Signs & Symptoms
Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases in which there are high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. It is caused either due to the pancreas not producing enough insulin or the body cells not responding properly to the insulin produced. As we all know, excess intake of sugar can cause diabetes and it is one of the most harmful diseases caused by sugar. The “World Diabetes Day” is celebrated on November 14 every year to raise awareness about the disease.
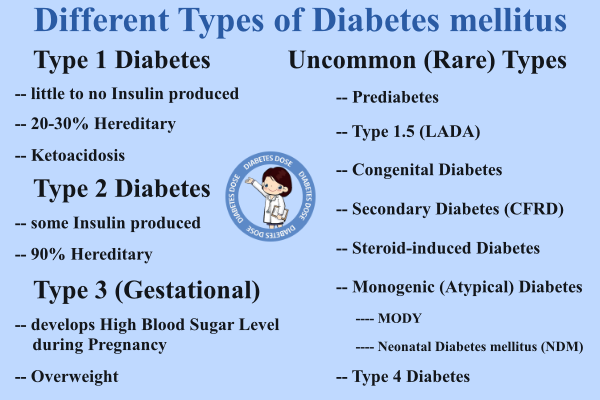
The Different Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes is caused because of pancreatic failure to produce enough insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes begins with insulin resistance. It is a condition where body’s cells fail to respond to insulin properly.
- Type 3 Diabetes, also called as Gestational Diabetes mellitus occurs when a pregnant woman without a prior history of diabetes develops high blood sugar level.
Signs and Symptoms
Many wonder about what are the first signs of diabetes to detect whether they are suffering from it because it is quite important to know about the early signs of diabetes and to recognize the symptoms of Diabetes correctly.
- The first signs of diabetes can be identified by weight loss, an increase in urination, thirst, and even hunger. But these symptoms usually develop slowly and can be absent in Type 2 Diabetes.
- Several other signs and symptoms in addition to the above ones include blurry vision, headache, fatigue, slow healing of cuts and itchy skin.
Diabetes Categorization – A Complete Guide
There are three major types of Diabetes with varying symptoms, effects and treatment methods. The two types of diabetes along with gestational diabetes mellitus (Type 3) are explained in detail below so that you have a sufficient knowledge about all of them.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes results from the failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin. This type of diabetes is due to loss of the insulin-producing beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. It can be further classified as immune-mediated or idiopathic. Most affected people are quite healthy when the first symptoms occur.
Type 1 Diabetes can affect both children and adults equally. It was traditionally called as “Juvenile Diabetes” because the majority of Type 1 Diabetes were found only in children. Signs of juvenile diabetes must be tracked and immediately acted upon for cure. These are some of the most prevalent diabetes symptoms in children.
One should know about symptoms of diabetes in children to take preventive measures before it strikes. Type 1 Diabetes can be accompanied by irregular and unpredictable high blood sugar levels, frequently with ketosis and sometimes low sugar levels. It is basically incurable but insulin injections will help in survival.
Signs of Type 1 Diabetes: Increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue and blurred vision.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, a condition where body cells fail to respond to insulin properly. The insulin receptor is believed to be involved in defective responsiveness of body tissue to insulin. It is said to be the most common type of Diabetes mellitus.
The major causes of Type 2 Diabetes are lifestyle factors and usually genetics. Obesity, lack of physical activity, poor diet, stress, and urbanization are known to be the developing factors for Type 2 Diabetes.
Excessive consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks and saturated fats are responsible for this type of diabetes. Cutting down on white rice can also help in the prevention. The difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes is that former one can occur at a young age whereas the latter one can strike in adulthood, the first signs start to develop mostly after the age 30.
Signs of Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive hunger, fatigue, or increased thirst, blurred vision, frequent urination, poor wound healing, or weight gain
Type 3 Diabetes
Type 3 Diabetes, also called as ‘Gestational Diabetes mellitus (GDM)‘ is a condition when a woman without any history of diabetes develops high blood sugar level during pregnancy. Type 3 Diabetes occurs to 2-10% of pregnant women and may improve or disappear after delivery.
Gestational Diabetes mellitus is fully treatable but it requires careful medical treatment and supervision throughout the tenure of pregnancy. If left untreated, it can cause severe and even fatal consequences.
Born babies to mother with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of being overweight, low blood sugar levels and jaundice. It can also result in stillbirth at times. In the long run, born babies can develop Type 2 Diabetes as well.
Gestational Diabetes mellitus is majorly caused by insufficient insulin in setting insulin resistance. Type 3 Diabetes can be prevented by maintaining a healthy diet and regular moderate exercise.
Signs of Type 3 Diabetes: Memory loss, dementia, and confusion. There may be no symptoms at early stages but the causes of diabetes for this type can be devastating.
Uncommon Types of Diabetes
There are also some uncommon types of diabetes that occurs in certain individuals with distinct symptoms as compared to Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. These diabetes types are even termed as ‘Rare Types of Diabetes‘.
Prediabetes
It indicates a condition that occurs when a person’s blood glucose levels are higher than normal but is not high enough for a diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes.
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA):
It is an autoimmune condition that usually develops in adults, often after the age of 30. This type of diabetes develops slower than normal Type 1 Diabetes.
Some cases of this diabetes are also noted where body’s tissue receptors do not respond to insulin even when insulin levels are normal, which is what separates it from Type 2 Diabetes.
This form of diabetes is quite uncommon as it has characteristics of both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Therefore, it is generally known as ‘Type 1.5 Diabetes‘.
Congenital Diabetes
The different forms of Diabetes mellitus also include Congenital Diabetes, which occurs due to genetic defects of insulin secretion.
Cystic Fibrosis-related Diabetes (CFRD)
It is a distinct type of diabetes that has been identified by relative insulin deficiency. Sometimes, it develops due to certain medications. This type of uncommon diabetes is also called as ‘Secondary Diabetes’.
It is a genetic disorder that normally occurs in individuals with cystic fibrosis. It results in the formation of thick mucus in lungs and other organs of infected person. This thick mucus can further damage the pancreas and bring down its ability to produce insulin that leads to diabetes.
Steroid-induced Diabetes mellitus
This type of rare diabetes is defined as the unusual increase in blood glucose that is induced by high doses of ‘Glucocorticoids‘ in a patient. It occurs in an individual who has or hasn’t a previous history of diabetes mellitus in its family.
Monogenic Diabetes
Single gene mutation is the main cause of Monogenic Diabetes. It majorly impacts on how the body uses or produces insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes comes under the category of ‘Atypical Diabetes’. It is categorized into two rare forms of diabetes that are as follows:
- MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young): This type of diabetes generally occurs in young adults or teens before the age of 25. It is inherited from any of the parents and distinguished by a genetic mutation that affects the production of insulin in the body.
- Neonatal Diabetes mellitus (NDM): This rare form of diabetes develops in infants or new-borns, especially in the first six months of life. It can be either permanent or temporary that totally depends on various factors.
Type 4 Diabetes
The ‘Type 4 Diabetes‘ is proposed but it has not received an official status yet.
One should know all about diabetes and even the major diabetes signs which will help in taking preventive measures in future.